soil
A high-tech enterprise focusing on the development and application of X-ray technology products, committed to becoming a leading supplier of X-ray industrial testing solutions.
Heavy Metals in Soil: What They Are and How to Test for Them—XRF technology
Soil health is essential for the growth of crops, the safety of the environment, and the well-being of all living organisms that rely on it. However, human activities—such as industrialization, mining, agriculture, and waste disposal—have led to the contamination of soil with heavy metals. These pollutants can pose significant risks to ecosystems, water quality, and human health. Fortunately, modern technology such as X-ray fluorescence (XRF) has made testing for heavy metals more accessible and efficient.

Terras EulerX900 Handheld Alloy Analyzer
Sources of Heavy Metal Contamination in Soil
Heavy metal contamination can come from both natural and human-made sources:
Industrial activities: Factories, power plants, and smelting operations often release heavy metals into the air and soil.
Agricultural practices: The use of contaminated pesticides, fertilizers, or irrigation water can introduce metals into the soil.
Mining and waste disposal: Mining operations, particularly in the extraction of precious metals like gold and copper, can lead to heavy metal leaching into the surrounding soil.
Why is Testing for Heavy Metals Important?
Testing for heavy metals is crucial for several reasons:
Public Health: Contaminated soil can lead to the contamination of food grown in the soil, which can, in turn, enter the human food chain.
Environmental Protection: Heavy metals can accumulate in the tissues of plants and animals, causing damage to ecosystems and biodiversity.
Regulatory Compliance: Many countries have established soil quality standards to limit the concentration of heavy metals in agricultural land. Testing ensures compliance with these standards.
Land Remediation: Identifying the extent of contamination can help inform the cleanup and restoration of polluted land.
How to Test for Heavy Metals in Soil?
Traditionally, testing for heavy metals in soil involved complex and time-consuming laboratory processes, such as atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) or inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). These methods, while highly accurate, can be expensive and require samples to be sent to a lab, which takes time.
Today, X-ray fluorescence (XRF) technology provides a much quicker, cost-effective, and non-destructive method for detecting heavy metals directly in the field.
XRF Technology: Revolutionizing Heavy Metal Testing
XRF is a powerful analytical technique that allows for the rapid and non-invasive detection of chemical elements in a sample. It works by exposing the sample to high-energy X-rays, which cause atoms in the material to emit secondary (or fluorescent) X-rays. These fluorescent X-rays are then analyzed to determine the presence and concentration of elements within the sample.
Advantages of XRF for Soil Testing
Real-time Results: XRF provides immediate analysis, allowing for on-site testing of soil without the need to wait for laboratory results.
Portable and Easy to Use: XRF analyzers are typically handheld, making them portable and easy to use in the field. This convenience is especially beneficial for large-scale agricultural monitoring or environmental surveys.
Non-destructive: XRF analysis does not require sample preparation or destruction, making it ideal for preserving samples for future testing or reuse.
High Sensitivity: XRF technology can detect heavy metals at very low concentrations, making it suitable for compliance with stringent environmental regulations.
Cost-Effective: Compared to traditional lab-based methods, XRF is generally less expensive, making it an attractive option for frequent testing or large-scale projects.
How XRF Testing Works in the Field
Prepare the Soil Sample: While XRF analysis does not require the sample to be ground into a fine powder like some lab methods, it’s important to remove debris and ensure a clean surface for testing.
Place the XRF Analyzer on the Sample: The analyzer is then held in contact with the soil sample or placed a short distance away.
Analyze the Results: The analyzer will emit X-rays, and within seconds, it will produce a spectrum of X-ray fluorescence that identifies the elements in the sample. The device will then display the concentrations of the heavy metals detected.
Interpret the Data: The results can be compared with local or international soil quality standards to assess whether the heavy metal levels are safe or exceed regulatory limits.
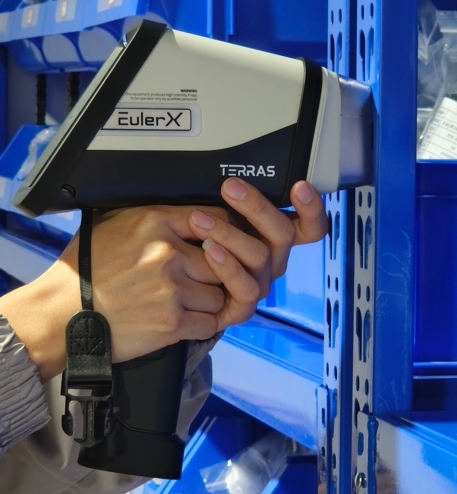

Terras EulerX900 Handheld Alloy Analyzer
The EulerX 900 series has proved to be an excellent choice for metal analysis in a wide fields, providing fast, accurate results directly to the user. Thanks to its cutting-edge electronics and sophisticated mathematical algorithms, the EulerX 900 series ensures superior measurement quality within seconds. This makes it an ideal tool for inspecting and analyzing incoming materials, finished products, and in-process production parts in a non-destructive manner. Its simplicity of operation allows users to quickly view alloy grade and chemical composition on the touch screen display, achieving laboratory-quality analysis with minimal training and virtually no need for sample preparation, regardless of the sample is shape or size.
Conclusion
Heavy metals in soil pose significant environmental and health risks, and detecting their presence is vital to maintaining soil quality and safety. Traditional testing methods can be costly and time-consuming, but XRF technology offers a faster, more affordable, and non-destructive alternative for field testing. As XRF analyzers continue to evolve and become more accessible, they are likely to play a crucial role in ensuring that soils remain safe for agriculture, wildlife, and human habitation.
Join Us
Subscribe to our email list for updates & promotions.