Alloy
A high-tech enterprise focusing on the development and application of X-ray technology products, committed to becoming a leading supplier of X-ray industrial testing solutions.
The Science Behind XRF Spectrometer Handheld Technology: A Beginner’s Guide
X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique used to determine the elemental composition of materials. Over the past few years, handheld XRF spectrometers have become an invaluable tool across various industries, from environmental testing to archaeology, mining, and even electronics. If you’ve ever wondered how these portable devices work or how they’re revolutionizing fields like material analysis, then this beginner’s guide is for you!
What is XRF Spectrometry?
XRF stands for X-ray fluorescence, a phenomenon in which atoms emit secondary (or fluorescent) X-rays when exposed to high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. By analyzing the energy and intensity of these fluorescent X-rays, scientists can identify the elements present in the sample and determine their concentrations.
In traditional laboratory settings, XRF spectrometers are large, stationary instruments, but the handheld versions are designed to be compact and portable, allowing for real-time analysis in the field. These devices typically combine the XRF technology with powerful microprocessors, making them accessible for both experts and non-specialists.

Terras EulerX900 Handheld Alloy Analyzer
How Does Handheld XRF Technology Work?
To understand how handheld XRF spectrometers work, it’s helpful to break down the process into a few key steps:
X-Ray Source: The handheld XRF spectrometer contains a small X-ray tube that generates high-energy X-rays when powered on. These X-rays are directed at the sample to be analyzed.
Excitation of the Sample: When the X-rays hit the atoms of the sample, they “excite” the atoms, knocking electrons from their inner shells. This creates vacancies in the atom’s electron shells.
Fluorescence Emission: To fill these vacancies, electrons from higher energy levels in the atom fall into the lower energy levels, releasing energy in the form of secondary X-rays. These secondary X-rays are specific to the elements present in the sample.
Detection and Analysis: The spectrometer’s detector captures these emitted fluorescent X-rays and analyzes their energy levels. Each element emits X-rays with unique energy signatures, allowing the spectrometer to identify and quantify the elements in the sample.
Results: Finally, the handheld device processes the data and displays a list of elements detected in the sample, often with their concentrations. This information can be reviewed instantly, providing real-time results that are invaluable in decision-making processes.
Key Components of Handheld XRF Spectrometers
Handheld XRF spectrometers are designed to be user-friendly and efficient, incorporating several important components:
X-Ray Tube: Generates the primary X-rays to excite the sample.
Detector: Measures the energy of emitted X-rays. Modern handheld devices often use silicon drift detectors (SDDs) because they are highly sensitive and accurate.
Filter: Filters out background radiation or non-relevant signals to improve the clarity and accuracy of measurements.
Display Screen: Shows the results, including elemental composition and concentration levels.
Battery and Power Management: Provides portable power to the device for field use.
Software: Advanced software algorithms process the raw data from the detector and provide clear, understandable results. This can include features like automatic calibration, on-site analysis, and reporting.
Advantages of Handheld XRF Spectrometers
The portability and ease of use of handheld XRF devices come with several notable advantages:
Portability: Traditional XRF spectrometers are bulky and require a laboratory setting, but handheld versions are lightweight and compact, making them ideal for on-site testing in environments like construction sites, mining operations, or archaeological digs.
Non-Destructive Testing: Unlike some analytical methods that require cutting, grinding, or chemically altering a sample, XRF spectrometry is non-destructive. This allows for repeated testing of the same sample without compromising its integrity.
Real-Time Results: One of the greatest advantages of handheld XRF spectrometers is that they provide immediate results. This is particularly important in industries where quick decisions are needed, such as quality control in manufacturing or environmental monitoring.
Ease of Use: Many handheld XRF spectrometers are designed with simplicity in mind, featuring user-friendly interfaces that allow individuals with minimal training to operate them. The results are often displayed directly on the device, simplifying the process.
Versatility: Handheld XRF spectrometers can be used for a wide range of applications, including alloy analysis, soil and water testing, precious metals identification, and even historical artifact preservation. They can detect a broad spectrum of elements, making them versatile tools in various industries.
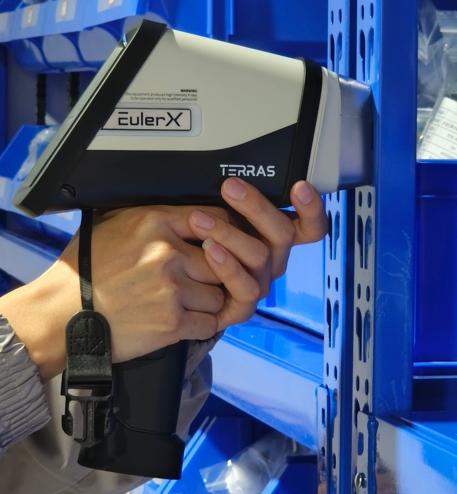

Terras EulerX900 Handheld Alloy Analyzer
The EulerX 900 series has proved to be an excellent choice for metal analysis in a wide fields, providing fast, accurate results directly to the user. Thanks to its cutting-edge electronics and sophisticated mathematical algorithms, the EulerX 900 series ensures superior measurement quality within seconds. This makes it an ideal tool for inspecting and analyzing incoming materials, finished products, and in-process production parts in a non-destructive manner.
Conclusion
Handheld XRF spectrometers are a fascinating and powerful tool that allows users to quickly and accurately identify the elemental composition of materials in real time. By leveraging the principles of X-ray fluorescence, these devices provide a non-destructive, portable, and easy-to-use solution for a wide range of industries, from environmental testing to archaeology. Whether you’re in the field of material science, mining, or quality control, handheld XRF technology is transforming the way we analyze and understand materials.
Join Us
Subscribe to our email list for updates & promotions.