Metal Material
A high-tech enterprise focusing on the development and application of X-ray technology products, committed to becoming a leading supplier of X-ray industrial testing solutions.
XRF Analysis Explained: How It Works and What It Can Do for You
Introduction
In today's fast-paced industrial world, material analysis has become crucial for quality control, safety compliance, and process optimization. X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) analysis has emerged as one of the most powerful and versatile techniques for elemental analysis. But what exactly is XRF, and how can it benefit your business or research? This comprehensive guide will explain the science behind XRF technology and explore its wide-ranging applications across various industries.
What is XRF Analysis?
XRF stands for X-ray Fluorescence, a non-destructive analytical technique used to determine the elemental composition of materials. Unlike other testing methods that require sample destruction, XRF allows you to analyze materials in their original state, making it ideal for quality control and precious material testing.

How Does XRF Work? The Science Made Simple
The XRF process follows these key steps:
Excitation: The analyzer emits high-energy X-rays that interact with the sample's atoms
Ejection: These X-rays dislodge inner-shell electrons from the atoms
Fluorescence: As outer-shell electrons fill the vacancies, they emit characteristic fluorescent X-rays
Detection: The analyzer measures the energy and intensity of these emitted X-rays
Analysis: Software identifies elements present and calculates their concentrations
Each element produces unique X-ray signatures, allowing for precise identification and quantification.
Types of XRF Analyzers
1. Energy Dispersive XRF (ED-XRF)
Simpler design
Simultaneous element detection
Good for general purpose analysis
2. Wavelength Dispersive XRF (WD-XRF)
Higher resolution
Better for light element detection
Typically more expensive
Key Advantages of XRF Technology
Non-destructive testing: Preserves sample integrity
Fast results: Analysis in seconds to minutes
Multi-element detection: Identifies many elements simultaneously
Minimal sample preparation: Often requires no special treatment
Portable options: Handheld units for field analysis
Applications Across Industries
1. Metals and Alloys
Grade verification
Positive Material Identification (PMI)
Scrap metal sorting
2. Mining and Geology
Ore grade analysis
Mineral exploration
Process control
3. Consumer Goods
RoHS compliance testing
Toy safety (lead, cadmium detection)
Jewelry authentication
4. Environmental
Soil contamination analysis
Air filter testing
Waste management
Choosing the Right XRF Solution
When selecting an XRF analyzer, consider:
Your specific application needs
Required detection limits
Sample types and sizes
Budget constraints
Portability requirements
The Future of XRF Technology
Recent advancements include:
Improved detection of light elements
Smaller, more portable designs
Enhanced data analysis with AI
Lower cost benchtop models
The EulerX 900 handheld XRF analyzer excels in alloy identification, scrap sorting, and PMI, delivering lab-accurate results in seconds. Its portability, ease of use, and no-prep design suit solids, liquids, and powders, revolutionizing quality control in metal processing and recycling with unmatched efficiency.
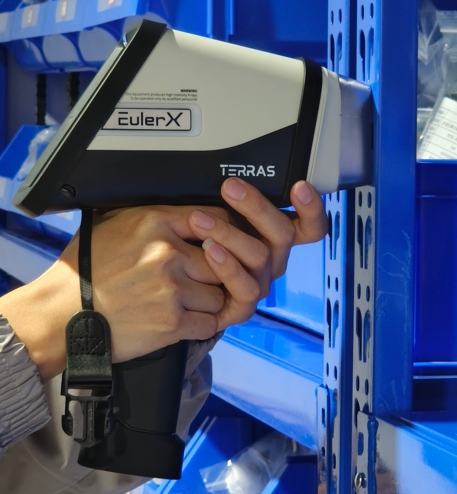

Terras EulerX900 Handheld Alloy Analyzer
Conclusion
XRF analysis offers a powerful, non-destructive solution for elemental analysis across numerous industries. From ensuring product safety to optimizing industrial processes, this versatile technology provides accurate, fast, and reliable results. Whether you're in manufacturing, mining, environmental testing, or quality control, understanding XRF capabilities can help you make informed decisions about material analysis in your operations.
Ready to explore how XRF can benefit your business? Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and demonstration.
Join Us
Subscribe to our email list for updates & promotions.